How are commands and configurations managed in Shinken¶
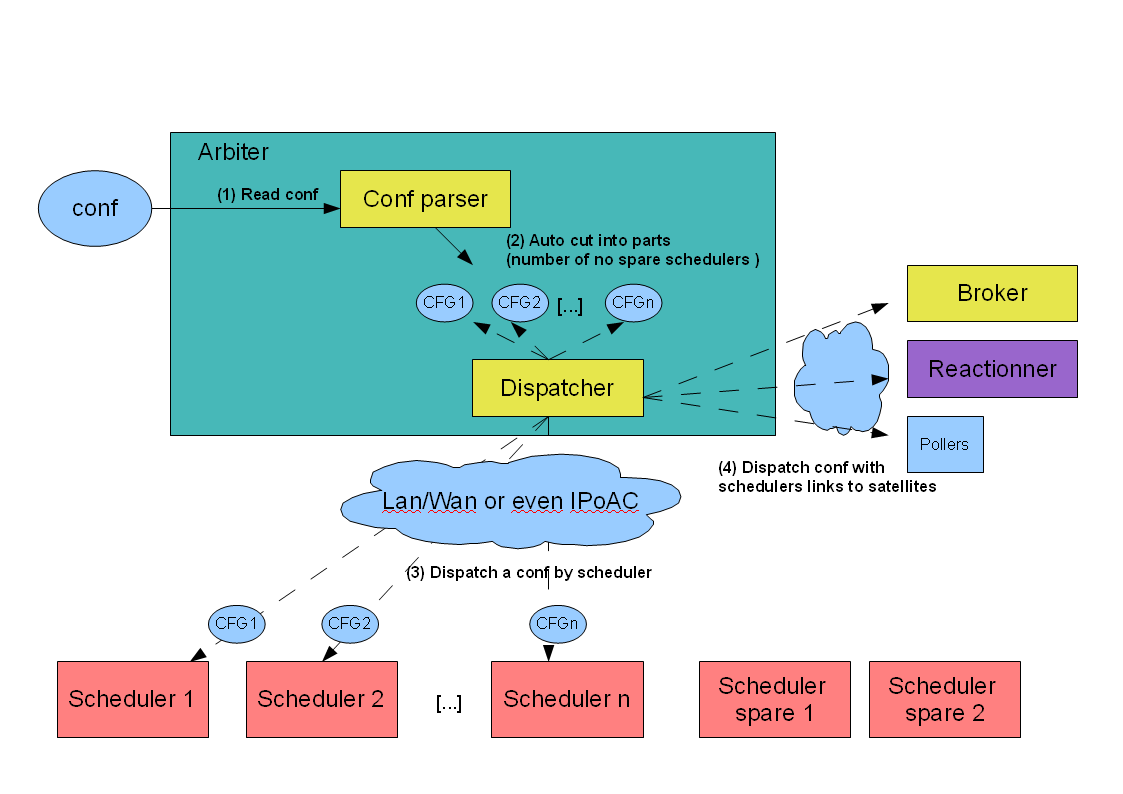
Let’s take a look at how the dispatching is managed.
Shinken uses different daemons: each one has it’s own task. The global master is the Arbiter: it reads the configuration, divides it into parts and sends the parts to various Shinken daemons. It also looks at which daemon are alive: if one dies, it will give the configuration of the dead one to another daemon so that it can replace it.
Configuration changes on running systems¶
Once the configuration is being dispatched to a Shinken process by the Arbiter, this causes the process (ex. Scheduler) to stop and reload its configuration. Thus for small configurations, the monitoring gap, where no monitoring is being done, is of an inconsequential duration. However, as the number of services rises above 10K and as the complexity of the configuration grows, the monitoring gap will become noticeable to the order of minutes. This gap will impact the type of SLA the monitoring solution can meet.
Important
The 1.2 release is mandatory for anyone using more than 10K services as it includes improvements addressing this issue.
External commands dispatching¶
Method 1 - Via the Arbiter daemon¶
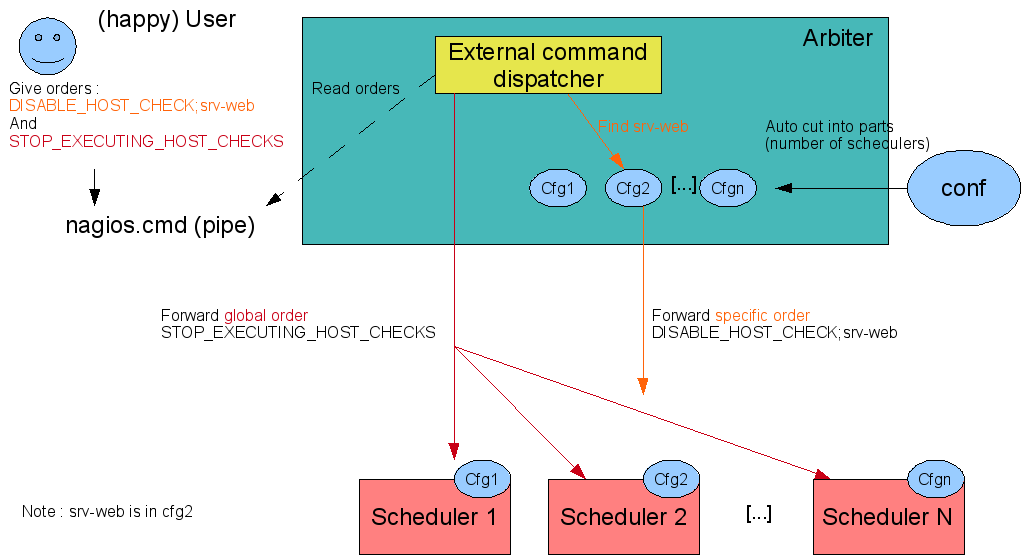
The user can send external commands to the system to raise a downtime or ask for passive checks. The commands should be sent to the only daemon that orchestrates everything in the system (the only one the user should know about): the Arbiter. It gives him the external commands (in a name pipe from now) and the Arbiter sends it to whoever needs it (just one scheduler or all of them).
It looks like this:
Method 2 - Via the Livestatus API¶
The Livestatus API is a Broker daemon module. It listens on the network for data requests or external commands. Commands can be authenticated. Commands can be submitted via a Python interface or a JSON interface. Consult the MK Livestatus documentation for the supported parameters.